Coastal Antarctic Permafrost Melting Faster Than Expected

Research team member Jim O'Connor of the USGS inspects a block of ice calved off the Garwood Valley ice cliff. Photo by Joseph Levy, University of Texas Institute for Geophysics.
For the first time, scientists have documented an acceleration in the melt rate of permafrost, or ground ice, in a section of Antarctica where the ice had been considered stable. The melt rates are comparable with the Arctic, where accelerated melting of permafrost has become a regularly recurring phenomenon, and the change could offer a preview of melting permafrost in other parts of a warming Antarctic continent.
Tracking data from Garwood Valley in the McMurdo Dry Valleys region of Antarctica, Joseph Levy, a research associate at The University of Texas at Austin's Institute for Geophysics, shows that melt rates accelerated consistently from 2001 to 2012, rising to about 10 times the valley's historical average for the present geologic epoch, as documented in the July 24 edition of Scientific Reports.
Scientists had previously considered the region's ground ice to be in equilibrium, meaning its seasonal melting and refreezing did not, over time, diminish the valley's overall mass of ground ice.
Instead, Levy documented through LIDAR and time-lapse photography a rapid retreat of ground ice in Garwood Valley, similar to the lower rates of permafrost melt observed in the coastal Arctic and Tibet.
Garwood Valley lies within the McMurdo Dry Valleys region of Antarctica. Image: Landsat Image Mosaic of Antarctica.
Ground ice is more prevalent in the Arctic than in Antarctica, where glaciers and ice sheets dominate the landscape. In contrast to glaciers and ice sheets, which sit on the ground, ground ice sits in the ground, mixed with frozen soil or buried under layers of sediment. Antarctica's Dry Valleys contain some of the continent's largest stretches of ground ice, along the coast of the Ross Sea.
After Levy and colleagues noted visible effects of ground ice retreat in Garwood Valley, they began to monitor the valley, combining time-lapse photography and weather-station data at 15-minute intervals to create a detailed view of the conditions under which the ice, a relict from the last ice age, is being lost.
Rising temperatures do not account for the increased melting in Garwood Valley. The Dry Valleys overall experienced a well-documented cooling trend from 1986 to 2000, followed by stabilized temperatures to the present.
Rather, Levy and his co-authors attribute the melting to an increase in radiation from sunlight stemming from changes in weather patterns that have resulted in an increase in the amount of sunlight reaching the ground.

Time-lapse imagery of ice loss in Garwood Valley, Nov. 2010 to Jan. 2012. The period represents the start and end of one summer season (Nov. 2010-Jan. 2011) followed by the end of the next season (Jan. 2012). The views were generated with biannual LiDAR scans of the valley. The University of Texas at Austin, Institute for Geophysics.
Sunlight tends to bounce off the white, reflective surfaces of glaciers and ice sheets, but the darker surfaces of dirty ground ice can absorb greater amounts of solar radiation. Thick layers of sediment tend to insulate deeply buried ground ice from sunlight and inhibit melting. But thin sediment layers have the opposite effect, effectively cooking the nearby ice and accelerating melt rates.
As the ground ice melts, the frozen landscape sinks and buckles, creating what scientists describe as "retrogressive thaw slumps." An acceleration in the prevalence of such slumps has been well documented in the Arctic and other permafrost regions, but not in Antarctica.
Levy's research shows that even under the stable temperature conditions of the Dry Valleys, recent increases in sunlight are leading to Arctic-like slump conditions.
If Antarctica warms as predicted during the coming century, the melting and slumping could become that much more dramatic as warmer air temperatures combine with sunlight-driven melting to thaw ground ice even more quickly.
Ground ice is not the major component of Antarctica's vast reserves of frozen water, but there are major expanses of ground ice in the Dry Valleys, the Antarctic Peninsula and the continent's ice-free islands.
Garwood Valley could tell the story of what will happen in these "coastal thaw zones," says Levy.
"There's a lot of buried ice in these low-elevation coastal regions, and it is primed to melt."
Co-authors on the paper were Andrew Fountain of Portland State University, James Dickson and James Head of Brown University, Marianne Okal of UNAVCO, David Marchant of Boston University and Jaclyn Watters of The University of Texas at Austin.
The research was supported by a grant from the National Science Foundation.
See the research paper at Scientific Reports:
Additional Images:

The Garwood Valley ice cliff. Scientists are about 50 meters in front of the cliff, which ranges from 10 to 15 meters tall. Photo by Jim O'Connor, USGS.
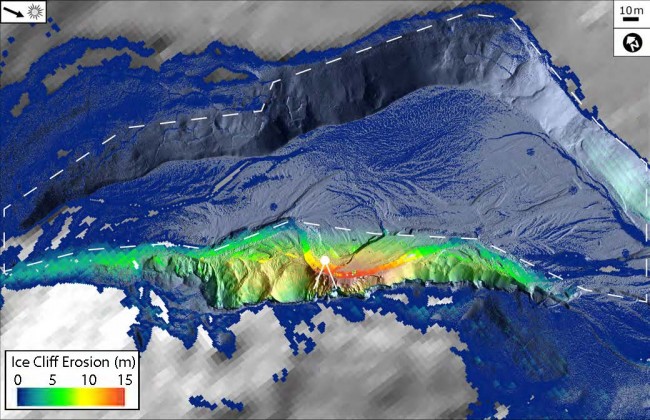
Ice cliff erosion since 2001. The solid white lines indicate infrared radiometer and sonic ranger field of view. Dashed line indicates area of erosion between initial ice/sediment deposition (Pleistocene/Holocene) and 2001. Image credit: Joseph Levy, University of Texas Institute for Geophysics.
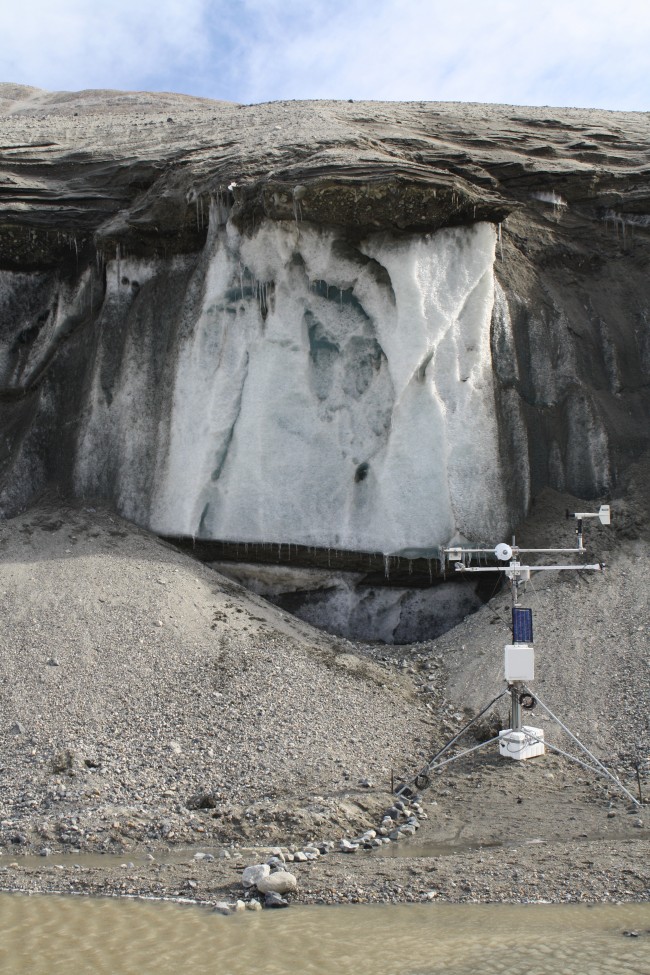

Meteorology station in front of a meltwater stream coming off the ice cliff and the Garwood River. Photo by Joseph Levy.



Ice loss at Garwood Valley ice cliff, Nov. 2010 to Jan. 2012. The period represents the start and end of one summer season (Nov. 2010-Jan. 2011) followed by the end of the next season (Jan. 2012). The views were generated with biannual LiDAR scans of the valley. The University of Texas at Austin, Institute for Geophysics.
--
__._,_.___
No comments:
Post a Comment