Maars and Phreatic Eruptions
A maar is a volcanic crater that forms when magma contacts ground water to produce a steam explosion.
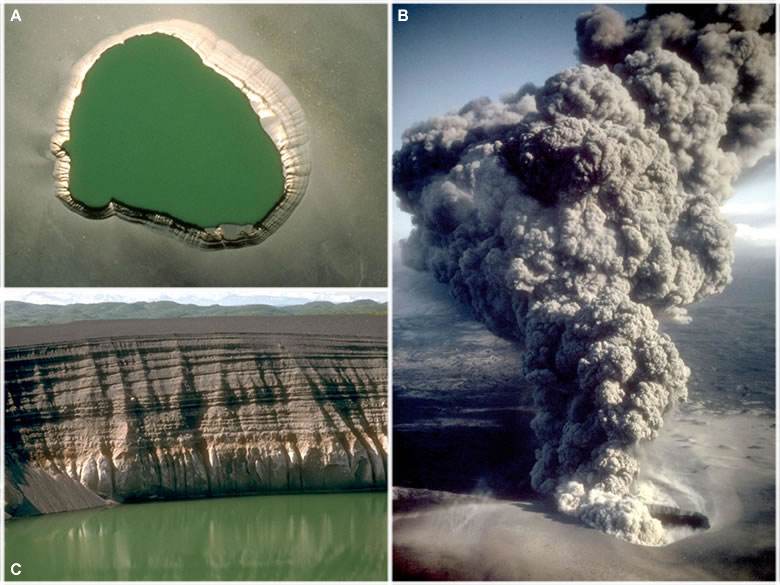

| Views of East Ukinrek Maar Crater, that formed in April, 1977 during a 10-day eruption. This eruption provided a rare - and the most recent - opportunity for researchers to observe the formation of a maar by volcanic activity. (A) A vertical view of the crater which is about 300 meters across. Not visible is a 49 meter-high lava dome within the crater that is now covered by water. The ground surrounding the crater is covered with tephra in this July 1990 photo by the Fish and Wildlife Service. Enlarge. (B) A photograph of the phreatomagmatic eruption and plume taken during the April, 1977 eruption. Image by the United States Geological Survey. Enlarge. (C) A view of the southeast crater wall showing stratified tephra deposits produced during the 1977 eruption. About 15 meters of tephra overlies a thin layer of glacial till that caps ash-flow deposits produced by an earlier eruption at Ugashik Caldera. Image by the United States Geological Survey. Enlarge. [1] |
What is a Maar?A maar is a shallow volcanic crater with steep sides that is surrounded by tephra deposits. The tephra deposits are thickest near the crater and decrease with distance from the crater.A maar is formed by one or more underground explosions that occur when hot magma comes into contact with shallow ground water to produce a violent steam explosion. These explosions crush the overlying rocks and launch them into the air along with steam, water, ash and magmatic material. The materials usually travel straight up into the air and fall back to Earth to form the tephra deposits that surround the crater. If the tephra lithifies it will become an igneous rock known as tuff. 
The crater floor of a maar is usually below the original ground surface. After the eruption an inflow of ground water often turns the crater into a shallow lake. Most maars are a few hundred to a thousand meters in diameter and less than one hundred meters in depth. The largest maars, located on the Seward Peninsula of Alaska, are up to 8000 meters across and up to 300 meters in depth. See Google map at right. How Common are Maars?Maars are more numerous than most people realize. After cinder cones, maars are the second most common volcanic landform. [2] If you search the Smithsonian Institution's Global Volcanism Program database, you will be able to find hundreds of maars. [3]Maars are underrepresented as volcanic landscape features because they are small in size and lack rocky vertical development that would make them resistant to weathering and erosion. Because they are relatively small, shallow depressions they can be easily infiled with sediments and not recognized as a volcanic features. Phreatic EruptionsThe explosions that form a maar are known as phreatic explosions. They are driven in part by the enormous and instantaneous volume change that occurs when water flashes into steam. When suddenly heated, one cubic meter of water converts into 1,600 cubic meters of steam. If this happens below Earth's surface the result can be a vertical eruption of steam, water, ash, volcanic bombs and rock debris. The volcanic cones produced by these eruptions are made up mostly of ejecta and are usually of very low relief - only a few tens of meters. Phreatomagmatic EruptionsSome magmas contain enormous amounts of dissolved gas -- sometimes up to several percent gas by weight. This gas is under very high confining pressure because the magma is below earth's surface. During a the formation of a maar the rock above the magma chamber is usually blasted away. This suddenly reduces the confining pressure on the magma and its dissolved gas. The sudden pressure reduction allows an immediate and violent expansion of the dissolved gas. The magma then degasses like a can of shaken beer when the pull tab is removed. When degassing magma adds to the explosive force the eruption is known as "phreatomagmatic". Not all phreatic and phreatomagmatic eruptions occur from the interaction of hot magma with ground water. Other water sources include: lakes, streams, the ocean or melting permafrost. Multiple ExplosionsMaars are usually formed by multiple explosions. Initially there can be simultaneous explosions at multiple depths. After the initial explosions, ground water from surrounding lands begins draining towards the crater and fuels additional blasts. These continue until the supply of local ground water is depleted or the magma source has been depleted or cooled. The 1977 eruption at the East Ukinrek Maar Crater, shown in the photos at the top of this page, consisted of a series of explosions that persisted for a period of ten days. The Largest Known MaarThe largest known maar on Earth is Devil Mountain Maar Lake, located on the northern part of the Seward Peninsula of Alaska. It was produced by a hydromagmatic eruption that occurred about 17,500 years ago. The blast spread tephra over an area of about 2,500 square kilometers. The tephra is several tens of meters thick near the maar and decreases with distance away from the maar. [4] You can explore five of the world's largest maars in the Google satellite image in the right column of this page. Contributor: Hobart King
http://geology.com/stories/13/maar/ | 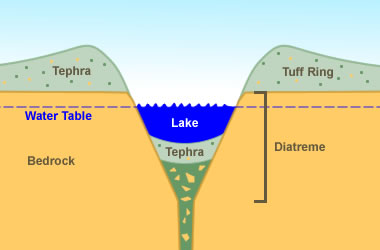


|
--
__._,_.___
No comments:
Post a Comment